The Red Screen of Death, also called RSOD, is a rare Windows crash. It can appear on Windows 10 or Windows 11. The screen turns red and shows a STOP code, like the one in the image you shared. This error stops Windows to prevent damage. Most of the time, it comes from GPU problems, driver issues, BIOS faults, or damaged system files.
This guide explains the causes and shows simple steps to fix RSOD and get your PC working again.
What Is the Red Screen of Death?
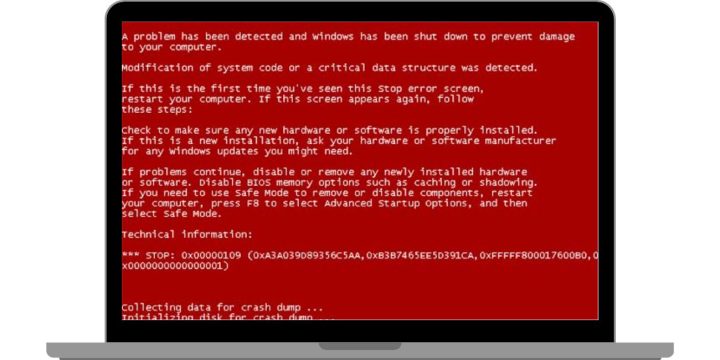
The Red Screen of Death is a crash screen that appears when Windows hits a serious system failure. It is less common than the Blue Screen of Death but usually means a deeper problem. RSOD often appears before Windows loads. It may also show up while gaming, updating drivers, or changing BIOS settings.
When Windows cannot recover, it stops and shows the red error screen.
Common Causes of RSOD
RSOD does not appear without reason. Here are some common triggers:
- A corrupted AMD, NVIDIA, or Intel GPU driver
- A bad graphics card firmware update
- Overheating from the CPU or GPU
- Wrong BIOS settings
- Failed overclocking
- Damaged system files
- Faulty RAM or GPU
- A failing SSD or HDD
- HDMI or DisplayPort handshake issues
Fixing RSOD means finding which area is unstable.
How to Fix the Red Screen of Death on Windows
If you are facing the Red Screen of Death on Windows, follow the steps below one by one. These steps help you fix the problem safely.
Fix 1. Restart Into Safe Mode
Safe Mode loads Windows with basic drivers only. This helps you undo changes that cause RSOD.
Steps:
- Hold Shift and select Restart
- Open Troubleshoot
- Choose Advanced options
- Select Startup Settings
- Pick Safe Mode
Once inside Safe Mode, uninstall bad drivers or undo any recent changes.
Fix 2. Remove or Reinstall GPU Drivers
GPU drivers cause most RSOD cases, especially on systems using AMD or NVIDIA cards. A broken driver blocks Windows from loading the graphics layer.
What to do:
- Boot into Safe Mode
- Open Device Manager
- Find Display adapters
- Uninstall your GPU driver
- Restart Windows and install a clean driver
If the issue repeats, use a clean install from AMD, NVIDIA, or Intel.
Fix 3. Undo GPU or CPU Overclocking
Overclocking tools like MSI Afterburner or Intel XTU can push hardware too far. This causes firmware or voltage errors that lead to RSOD.
Fix this by:
- Resetting GPU settings to default
- Resetting CPU settings to default
- Avoiding custom voltage or custom fan curves
If the RSOD stops, the overclock was the cause.
Fix 4. Reset BIOS or UEFI to Default
Bad BIOS settings lead to RSOD, especially wrong memory timings or unstable XMP profiles.
To reset BIOS:
- Restart your computer
- Press your BIOS key (F2, F10, Delete, Esc)
- Load Setup Defaults
- Save and exit
This restores stable factory settings.
Fix 5. Run SFC, DISM, and CHKDSK
Corrupted system files create kernel errors that trigger RSOD.
Run these tools:
SFC:
- sfc /scannow
DISM:
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
CHKDSK:
- chkdsk /f /r
These tools repair Windows system files, the system image, and disk errors.
Fix 6. Update BIOS, GPU Firmware, or Motherboard Drivers
Old firmware causes problems with GPUs, RAM, and PCI devices. This can trigger RSOD on boot or while gaming.
Check for:
- BIOS updates on your motherboard page
- GPU firmware updates from NVIDIA or AMD
- Chipset driver updates from Intel or AMD
Install updates carefully and restart.
Fix 7. Disconnect or Test Hardware
Loose or damaged hardware can cause RSOD. GPU or RAM problems create memory and firmware errors.
Try these steps:
- Reseat RAM sticks
- Reseat the GPU
- Test with one RAM stick at a time
- Check HDMI or DisplayPort cables
- Disconnect extra USB devices
- Test with a different PSU if available
If RSOD stops after removing one part, the faulty hardware was the cause.
Fix 8. Use Windows Recovery Tools
If Windows still shows a red screen, use recovery tools.
Try:
- Startup Repair
- System Restore
- Booting from a USB installer
- Repairing the boot files
- Reset This PC (last resort)
These tools can restore Windows when normal fixes fail.
Conclusion
The Red Screen of Death may look scary, but most causes can be fixed. GPU drivers, BIOS settings, system files, or faulty RAM often trigger it. Safe Mode, clean driver installs, BIOS resets, and repair tools usually solve the problem.
If one of these steps helped your system, feel free to share your experience so others can fix their RSOD issue too.

