A CSV file is one of the simplest and most common ways to store and share data. It’s often used for tables, lists, or databases. If you’ve ever exported contacts, sales data, or reports from a website or app, you’ve probably seen a file ending in .csv.
In this guide, you’ll learn what a CSV file is, how it works, how to open it, and how it’s different from Excel files.
What Is a CSV File?
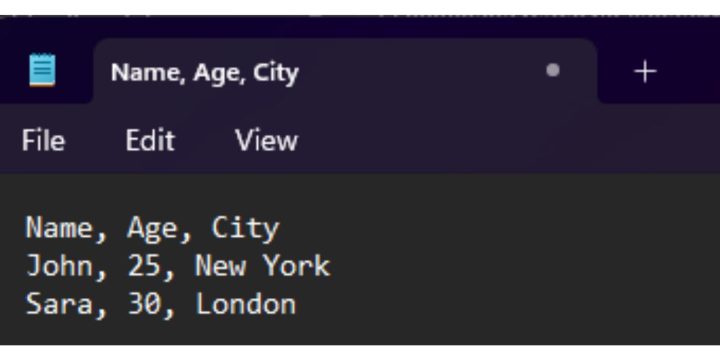
CSV stands for Comma-Separated Values. It’s a plain text file that stores data in a simple table format. Each line in the file represents a row, and each comma separates one column from another.
Here’s a basic example:
Name, Age, City
John, 25, New York
Sara, 30, London
Each value is separated by a comma, and together they form a neat table when opened in a spreadsheet.
Key points:
- CSV files store data using plain text.
- Each comma separates fields or columns.
- There’s no formatting, colors, or formulas — only raw data.
How CSV Files Work
CSV files organize data into rows and columns using simple text. The first line often contains column names (headers), and the lines below contain the data itself.
Example (text view):
Product, Price, Quantity
Apple, 1.2, 10
Banana, 0.8, 25
When you open it in Excel or Google Sheets, it appears like this:
| Product | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | 1.2 | 10 |
| Banana | 0.8 | 25 |
Some CSV files use semicolons (;) or tabs instead of commas, depending on language and software settings.
How to Open a CSV File
You can open a CSV file with almost any spreadsheet or text program. It doesn’t require special software.
Common options include:
- Microsoft Excel – Opens CSV files automatically in table format.
- Google Sheets – Upload or import a CSV to view it online.
- Text Editors – Like Notepad or VS Code (shows plain text).
- Database Tools – Such as MySQL or PostgreSQL for structured imports.
Even though CSVs are plain text files, programs like Excel automatically arrange them into columns for easier reading.
How to Create or Edit a CSV File
You can make or edit a CSV file using Excel, Google Sheets, or even a simple text editor.
Steps to create one:
- Open Excel or Google Sheets.
- Enter your data in rows and columns.
- Click File → Save As (or Download As in Sheets).
- Choose CSV (.csv) as the file type.
When you save it, all formatting, colors, and formulas are removed — only text and numbers stay.
Common Uses for CSV Files
CSV files are widely used across industries due to their compact size, simplicity, and compatibility with most software.
You might use a CSV file to:
- Import or export contact lists.
- Move data between apps like Excel, Google Sheets, or databases.
- Upload product catalogs or reports to websites.
- Store structured data from analytics tools.
Because CSVs are universal, they make sharing data easy between different programs and systems.
CSV vs Excel Files
While both store data in rows and columns, they’re not the same.
| Feature | CSV | Excel (.xlsx) |
|---|---|---|
| Format Type | Plain text | Binary file |
| Supports Formulas | No | Yes |
| Saves Formatting | No | Yes |
| File Size | Small | Larger |
| Compatibility | Works everywhere | Requires an Excel-compatible app |
CSV is best for quick data exchange. Excel is better for complex calculations, charts, and formatting.
Advantages and Limitations of CSV Files
Advantages:
- Small file size and easy to share.
- Works with most software and platforms.
- Simple to edit and understand.
Limitations:
- No formatting, colors, or charts.
- Can’t handle multiple sheets.
- Errors may occur if data contains commas or special characters.
CSV files are great for storing clean, simple data — not for fancy spreadsheets or detailed reports.
Conclusion
A CSV file is a lightweight and widely supported file format that stores tabular data in plain text. Each comma separates the values, making it simple for computers and humans to read.
It’s perfect for data exchange, imports, and backups — and can be opened almost anywhere. While it lacks features like formulas or formatting, its simplicity makes it one of the most flexible file types for everyday data use.

